Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Wakui, Takashi; Takagishi, Yoichi*; Futakawa, Masatoshi
Materials, 16(17), p.5830_1 - 5830_16, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Physical)Cavitation damage on the mercury target vessel is induced by proton beam injection in mercury. The prediction method of the cavitation damage using Monte Carlo simulations was proposed taking into account of the uncertainties of the position of cavitation bubbles and impact pressure distributions. The distribution of impact pressure attributed to individual cavitation bubble collapsing was assumed to be the Gaussian distribution, and the probability distribution of the maximum value of impact pressures was assumed to be three kinds of distributions; the delta function, the Gaussian and Weibull distributions. Two parameters were estimated using Bayesian optimization by comparing the distribution of the cavitation damage obtained from experiment with that of accumulated plastic strain obtained from the simulation. It was found that the results obtained using the Weibull distribution reproduced the actual cavitation erosion phenomenon better than the other results.
Narukawa, Takafumi; Hamaguchi, Shusuke*; Takata, Takashi*; Udagawa, Yutaka
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 411, p.112443_1 - 112443_12, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Wakui, Takashi; Takagishi, Yoichi*; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Tanabe, Makoto*
Jikken Rikigaku, 23(2), p.168 - 174, 2023/06
Cavitation damage on the inner surface of the mercury target for the spallation neutron source occurs by proton bombarding in mercury. The prediction method of the cavitation damage using Monte Carlo simulations was suggested taking variability of the bubble core position and impact pressure distribution into account. The impact pressure distribution was estimated using the inverse analysis with Bayesian optimization was conducted with comparison between cavitation damage distribution obtained from experiment and the cumulative plastic strain distribution obtained from simulation. The average value and spread of maximum impact pressure estimated assuming the Gaussian distribution were 3.1 GPa and 1.2  m, respectively. Simulation results reproduced experimental results and it can be said that this evaluation method is useful.
m, respectively. Simulation results reproduced experimental results and it can be said that this evaluation method is useful.
Narukawa, Takafumi; Hamaguchi, Shusuke*; Takata, Takashi*; Udagawa, Yutaka
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2022 (ASRAM 2022) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2022/12
Narukawa, Takafumi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 63(11), p.780 - 785, 2021/11
, 63(11), p.780 - 785, 2021/11
no abstracts in English
Sugiyama, Daisuke*; Nakabayashi, Ryo*; Tanaka, Shingo*; Koma, Yoshikazu; Takahatake, Yoko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(4), p.493 - 506, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:30.55(Nuclear Science & Technology)Narukawa, Takafumi; Yamaguchi, Akira*; Jang, S.*; Amaya, Masaki
Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management (PSAM-14) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2018/09
Narukawa, Takafumi; Yamaguchi, Akira*; Jang, S.*; Amaya, Masaki
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 331, p.147 - 152, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:29.78(Nuclear Science & Technology)Yokoyama, Kenji; Yamamoto, Akio*; Kitada, Takanori*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(3), p.319 - 334, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:62.29(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new formulation of the cross-section adjustment methodology with the dimensionality reduction technique has been derived. This new formulation is proposed as the dimension reduced cross-section adjustment method (DRCA). Since the derivation of DRCA is based on the minimum variance unbiased estimation (MVUE), an assumption of normal distribution is not required. The result of DRCA depends on a user-defined matrix that determines the dimension reduced feature subspace. We have examine three variations of DRCA, namely DRCA1, DRCA2, and DRCA3. Mathematical investigation and numerical verification have revealed that DRCA2 is equivalent to the currently widely used cross-section adjustment method. Moreover, DRCA3 is found to be identical to the cross-section adjustment method based on MVUE, which has been proposed in the previous study.
Narukawa, Takafumi; Yamaguchi, Akira*; Jang, S.*; Amaya, Masaki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 499, p.528 - 538, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:62.29(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Lu, K.; Miyamoto, Yuhei*; Mano, Akihiro; Katsuyama, Jinya; Li, Y.
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2017 (ASRAM 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2017/11
Nowadays, probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) has been utilized in several countries as a rational method for structural integrity assessment of important structural components such as reactor pressure vessels (RPVs). In PFM analyses, potential flaws in target components are used to evaluate the failure probability or frequency. Therefore, flaw distributions (i.e., flaw depth and density distributions) in an RPV shall be rationally set as one of the most important influential factors, which are developed during the manufacturing process such as welding. Recently, a Bayesian updating methodology was applied to reflect the inspection results into flaw distributions, and the likelihood functions applicable to the case when flaws are detected in inspections were proposed. However, there may be no flaw indication as the inspection results of some RPVs. The flaw distributions in this situation are important while the corresponding likelihood functions have not been proposed. Therefore, this study proposed likelihood functions to be applicable for both case when flaws are detected and when there is no flaw indication as the inspection results. Based on the proposed likelihood functions, several application examples were given in which flaw distributions were estimated by reflecting the inspection results through Bayesian update. The results indicate that the proposed likelihood functions are useful for estimating the flaw distribution for the case when there is no flaw indication as the inspection results.
Zheng, X.; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2017 (ASRAM 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 11 Pages, 2017/11
Zheng, X.; Ishikawa, Jun; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 49(2), p.434 - 441, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:36.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)Chimi, Yasuhiro; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Kasahara, Shigeki*; Iwata, Keiko; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 307, p.411 - 417, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)To investigate influential parameters for irradiation-assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) growth behavior, we attempt to analyze statistically existing data on the crack growth rate (CGR) in irradiated austenitic stainless steels (SSs) in boiling water reactor (BWR) environments using the Bayesian nonparametric (BNP) method. From the probability distribution of CGR and some input parameters, such as yield stress of irradiated material (
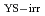 ), stress intensity factor (
), stress intensity factor ( ), electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP), and fast neutron fluence, the mean CGR is estimated and compared with the measured CGR. The analytical results show good reproducibility of the measured CGR. The results also indicate the possible neutron fluence effects on CGR in high CGR region (i.e., high neutron fluence condition) by radiation-induced segregation (RIS), localized deformation, and/or other mechanisms than radiation hardening.
), electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP), and fast neutron fluence, the mean CGR is estimated and compared with the measured CGR. The analytical results show good reproducibility of the measured CGR. The results also indicate the possible neutron fluence effects on CGR in high CGR region (i.e., high neutron fluence condition) by radiation-induced segregation (RIS), localized deformation, and/or other mechanisms than radiation hardening.
Zheng, X.; Ishikawa, Jun; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of 13th Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management Conference (PSAM-13) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2016/10
Zheng, X.; Ito, Hiroto; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Maruyama, Yu
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(3), p.333 - 344, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:67.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)Zheng, X.; Ito, Hiroto; Kawaguchi, Kenji; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Maruyama, Yu
Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 138, p.253 - 262, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:39.75(Engineering, Industrial)Haruyama, Mitsuo; Takase, Misao*; Iwasaki, Shin*; Tobita, Hiroshi
JAERI-Research 2002-022, 91 Pages, 2002/12
In the course of research on quantitative assay of non-destructive measurement of radioactive waste, the authors have developed a unique program based on the Bayesian theory for reconstruction of transmission computed tomography (TCT) image. The reconstruction of cross-section images in the CT technology usually employs the Filtered Back Projection method. The new imaging reconstruction program reported here is based on the Bayesian Back Projection method, and it has a function of iterative improvement images by every step of measurement. Namely, this method has the capability of prompt display of a cross-section image corresponding to each angled projection data from every measurement. Hence, it is possible to observe an improved cross-section view by reflecting each projection data in almost real time. The present reconstruction program developed here for the  -ray CT can widely applied also to, for instance, the Neutron Imaging and the Positron Emission Tomography (PET).
-ray CT can widely applied also to, for instance, the Neutron Imaging and the Positron Emission Tomography (PET).
Yamaguchi, Akira
PNC TN9410 94-070, 51 Pages, 1994/02
Seismic fragilities of equipment and systems are evaluated in a seismic probabilistic safety analysis (PSA). The seismic fragility is defined as the failure probability and its uncertainty at various ground acceleration levels. One evaluates the seismic fragility efficiently by making most use of available information in the seismic PSA. This study is related to a Bayesian inference method to reflect the information to the seismic fragility evaluation. Information that can be used in the Bayesian inference is (1)seismic experience data, (2)expert judgment on the seismic fragility, (3)seismic test data. The generic fragility database was used as the prior fragility that was to be updated. The acceleration level of the seismic experience and test data is much lower than the median value of the seismic capacity level of equipment. However, it is useful to cut down the lower tail of the fragility curves thus the modeling uncertainty. As the results, it is has been found that the annual frequency of failure that is calculated by the convolution of the fragility with seismic hazard curves is reduced considerably. Furthermore, the author has proposed the concept of entropy to quantify the value of the information used in the Bayesian inference. The combined use of the Bayesian inference and the entropy is a useful method to propose a cost-effective seismic test for the fragility evaluation. Findings obtained from the seismic PSA are taken into consideration in achieving more reasonable safety design. It should be noted that the findings are strongly affected by the uncertainty. Hence the reduction is necessary of the uncertainty of the contributive equipment from the viewpoint of seismic safety. Specific analysis and test of the contributive equipment is an effective way of reducing the uncertainty.
Murakami, Haruko*; Sun, D.*; Seki, Akiyuki; Takemiya, Hiroshi; Saito, Kimiaki
no journal, ,
This study presents a Bayesian hierarchical method to integrate multiple types of radiation measurements and to estimate the spatiotemporal distribution of radiation air dose rates around the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. The method incorporates the temporal evolution of dose rates by separating the log-linear decay trend and the fluctuations of air dose rates which are spatially correlated based on adjacent monitoring post data.
Muramatsu, Ken; Kubo, Kotaro; Takada, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English